7 LOHMANN, U. 2010: Holzlexikon, Photosynthese (4)
Hamburg: Nikol Verlag, Page 914
8 BMI 2019: Life Cycle Assessment, database
<https://www.oekobaudat.de/datenbank/
browser-oekobaudat.html>
accessed 20 July 2019
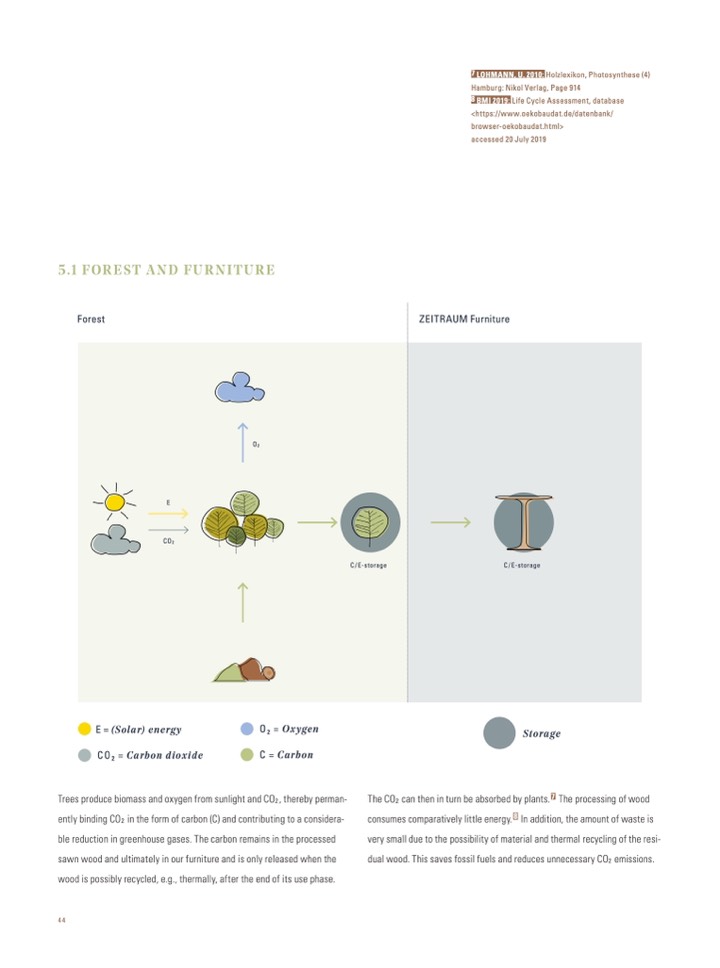
5.1 FOREST AND FURNITURE
Forest
ZEITRAUM Furniture
O
2
E
CO
2
C / E-storage
C / E-storage
E = (Solar) energy
CO
2
= Carbon dioxide
O
2
= Oxygen
C = Carbon
Storage
The CO
2
can then in turn be absorbed by plants.7 The processing of wood
consumes comparatively little energy. 8 In addition, the amount of waste is
very small due to the possibility of material and thermal recycling of the resi-
dual wood. This saves fossil fuels and reduces unnecessary CO
2
emissions.
Trees produce biomass and oxygen from sunlight and CO
2
, thereby perman-
ently binding CO
2
in the form of carbon (C) and contributing to a considera-
ble reduction in greenhouse gases. The carbon remains in the processed
sawn wood and ultimately in our furniture and is only released when the
wood is possibly recycled, e.g., thermally, after the end of its use phase.
44